Slides: Visualization with seaborn
- I Visualization statistical relationships (“relplot”)
- II Visualization of distributional data (“displot”)
- III Visualization of categorical data (“catplot”)
I Visualization statistical relationships (“relplot”)
replot()
- scatterplot() (with kind=“scatter”; the default)
- lineplot() (with kind=“line”): consecutive points will be linked by a line segment. To emphasize continuity between consecutive points
Scatter plots are close to 2-dimensional distributional plots
II Visualization of distributional data (“displot”)
1-d dimensional data:
- displot()
- histplot() with kind=“hist”
- kdeplot() with kind=“kde”
- ecdfplot() with kind=“ecdf” (empirical distribution function)
II Visualization of distributional data (“displot”)
2-d distributional plots
- displot()
- specify both
x=andy=
- specify both
- jointplot()
- kind=‘hex’ or kind=‘hist’ for 2d histograms/heatmaps
- kind=‘kde’
III Visualization of categorical data (“catplot”)
Categorical scatter plots:
- stripplot() (with kind=“strip”; the default)
- swarmplot() (with kind=“swarm”)
Categorical distribution plots:
- boxplot() (with kind=“box”)
- violinplot() (with kind=“violin”)
- boxenplot() (with kind=“boxen”)
Categorical estimate plots:
- pointplot() (with kind=“point”)
- barplot() (with kind=“bar”)
- countplot() (with kind=“count”)
I Visualization statistical relationships (“relplot”)
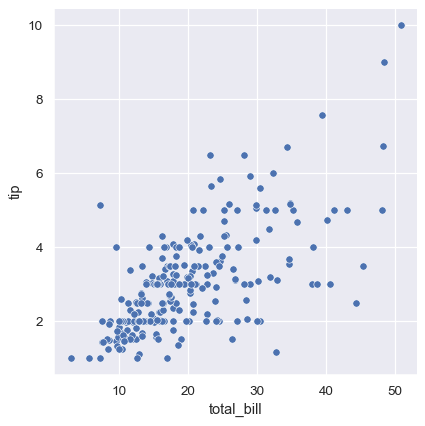
Simple scatter plot
Simple scatter plot: different colors for different categorical value
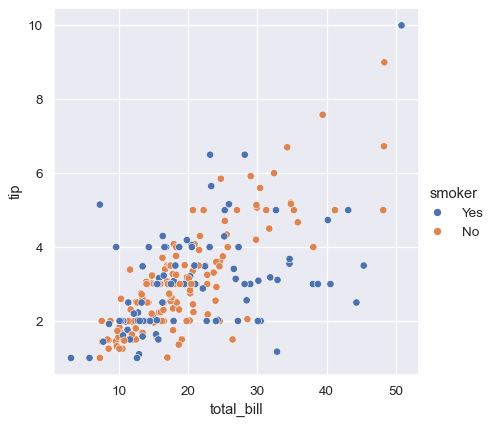
Different colors/markers based on categorical values
Add information about a third variable with color
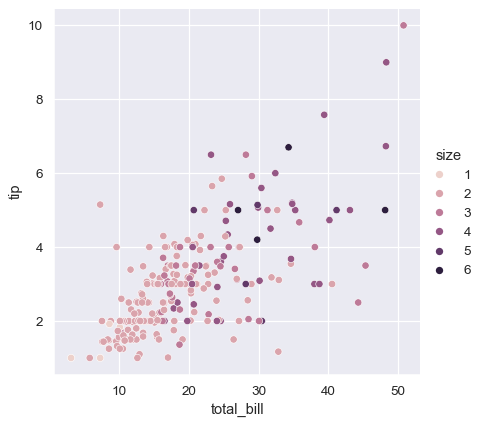
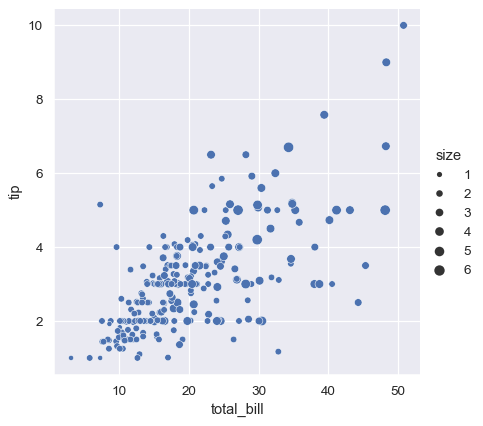
Add information about a third variable with size
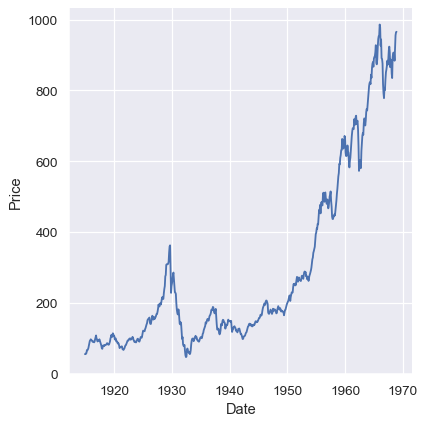
Line plots to emphasize continuity
Stock prices
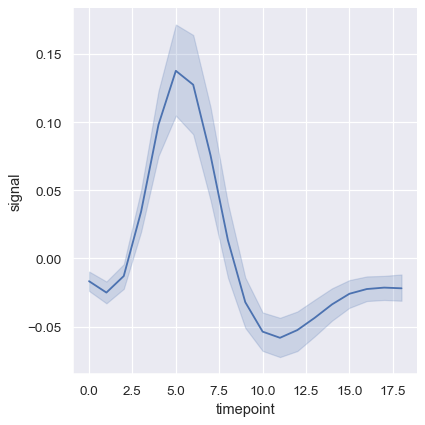
fMRI measurements (x-axis is time), several signals for each value of x
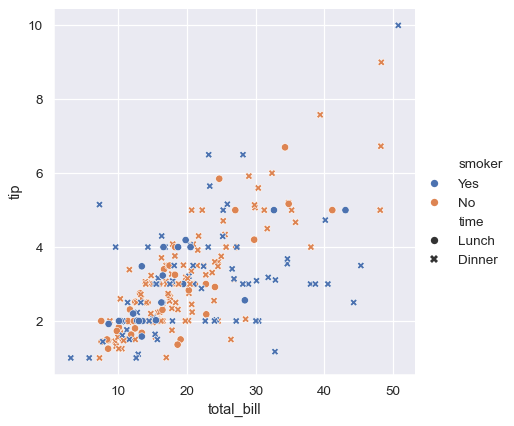
Plotting samples from different categories on different subplots
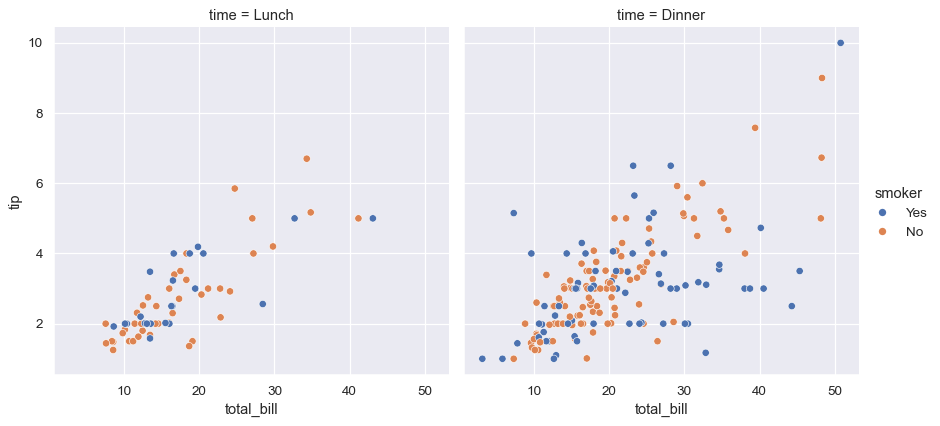
Plotting samples from different categories with different colors and styles
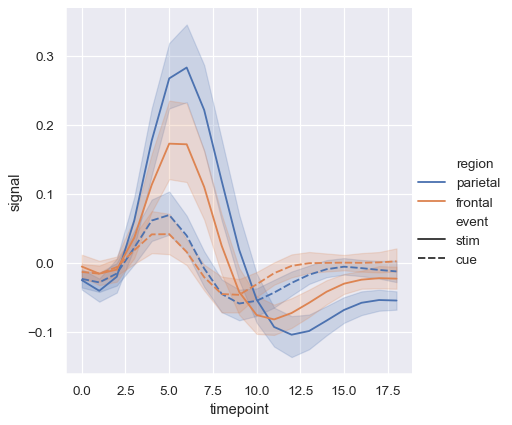
II Visualization of distributional data (“displot”)
Visualization of distributional data (“displot”)
1-d dimensional data:
- displot()
- histplot() with kind=“hist”
- kdeplot() with kind=“kde”
- ecdfplot() with kind=“ecdf” (empirical distribution function)
2-d distributional plots
- displot()
- specify both
x=andy=
- specify both
- jointplot()
- kind=‘hex’ or kind=‘hist’ for 2d histograms/heatmaps
- kind=‘kde’
Histogram with continuous data

Histogram with discrete data (“party size”)
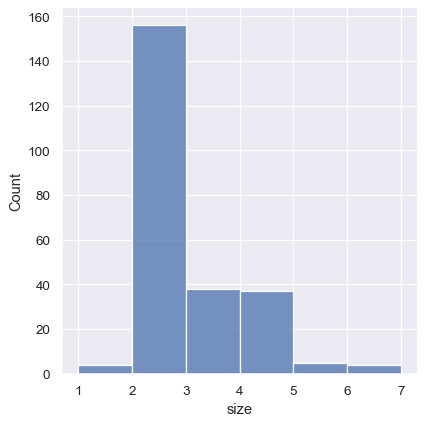
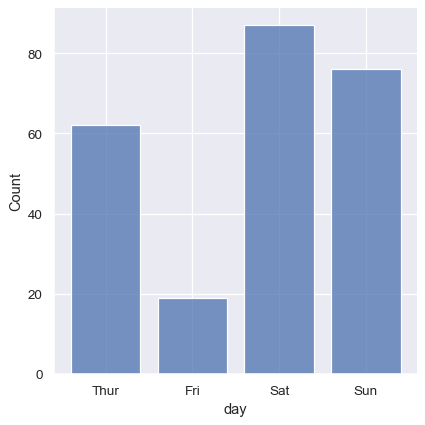
Histogram with discrete data (weekdays)
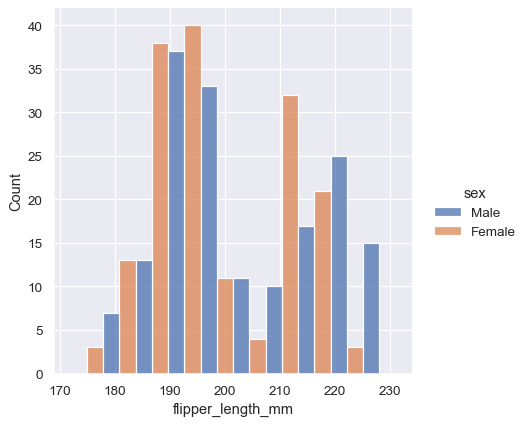
Distribution of data differentiated based on categorical variable
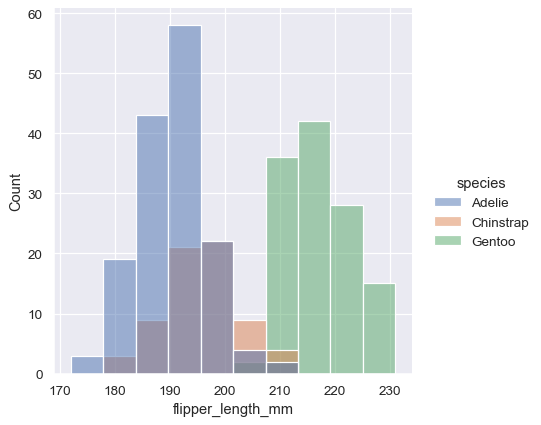
Histogram stacking versus histogram overlap
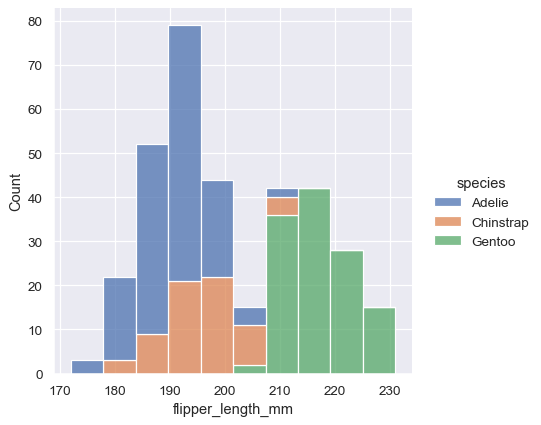
Histogram stacking versus histogram overlap versus dodge
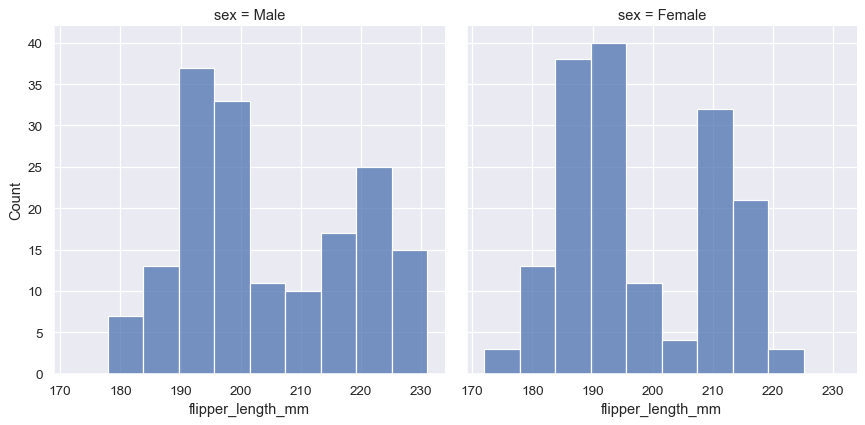
Different subplots for different value on a categorical variable
2-dimensional distributional plots
Histograms in 2d
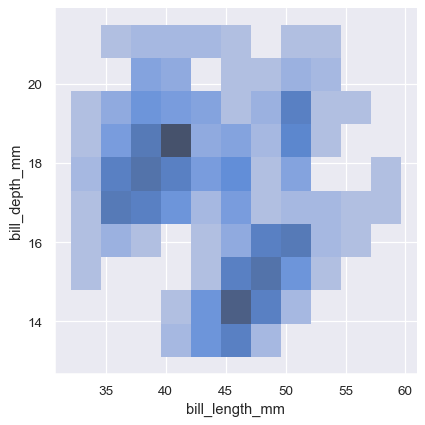
KDE plots in 2d

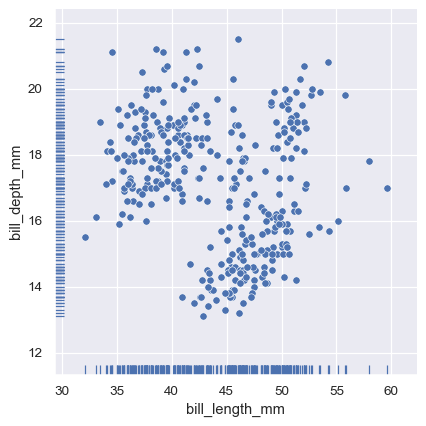
2d histograms differentiated with colors for different species
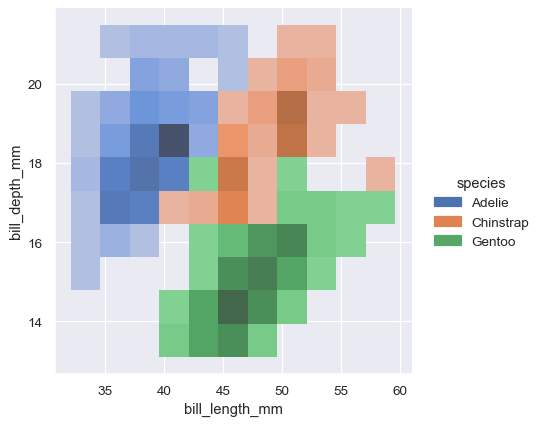
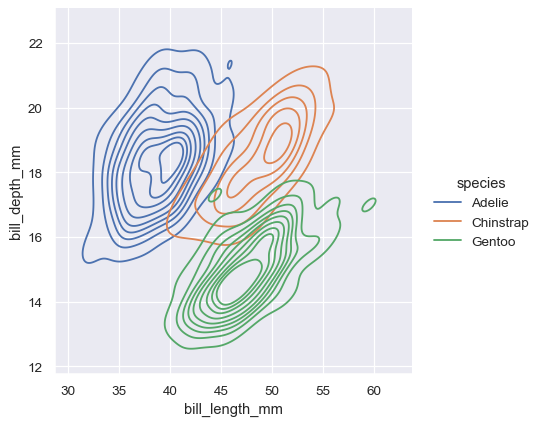
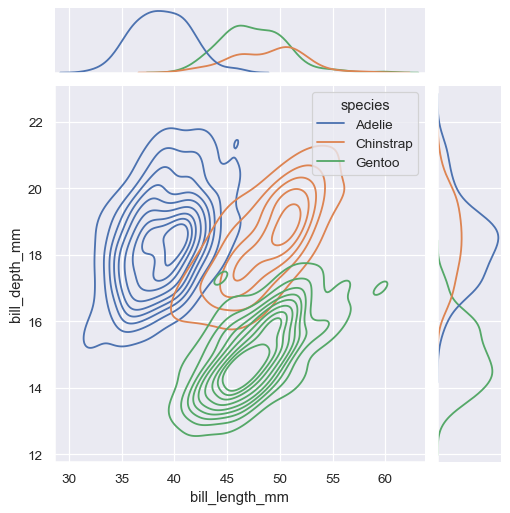
2d KDE plots differentiated with colors for different species
visualizing 2d distributions and 1d marginals
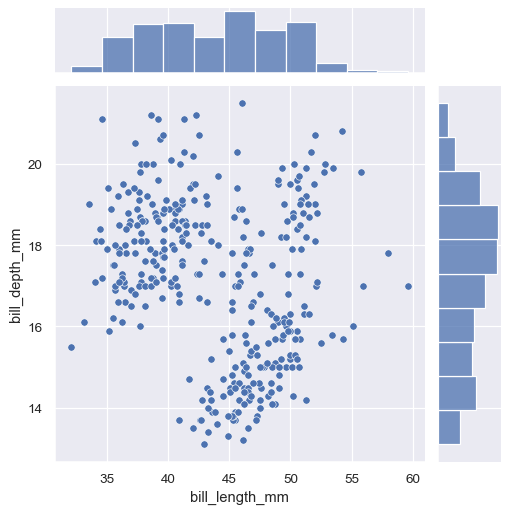
visualizing 2d distributions and 1d marginals
Rug: visualizing 2d dist AND 1d locations of single points